The world wide web consists of over 1.7 billion websites and over 2.76 billion pages. To access these websites and pages, 5 billion Internet users rely on user interfaces (UI). A web UI enables users to interact with websites and web applications via a browser; thus, clearly, websites and UIs are closely intertwined, and you can’t have one without the other.
But to build a user-friendly UI that people will want to use, website developers need the right UI development framework. About 95% of websites are developed using JavaScript frameworks, and one of the most versatile and popular types of JavaScript frameworks available today is Vue.js.

JavaScript Frameworks
The best JavaScript frameworks provide numerous tools to build scalable, interactive, highly dynamic web applications without having to start from scratch. They include code libraries to effortlessly define the structure of the entire application. With pre-written code and routine programming features, JavaScript frameworks simplify app development. They also allow for greater predictability and homogeneity in applications. Some of the most popular JavaScript frameworks available are:
- AngularJS: This open-source web application framework uses declarative HTML templates and leverages HTML vocabulary on dynamic web pages.
- React: A library for rendering UI components that’s usually used with ReactDOM to build web applications.
- Ember.js: Employing a component-service pattern, this older JS framework is still quite popular due to its stability and community support.
And then there’s Vue.js. As inferred above, the feature-rich, user-friendly Vue.js JavaScript framework has been increasing in popularity. Let’s find out why!
What is Vue.js?
Vue.js is a progressive JavaScript framework that allows for the construction of front-end web UIs. It builds on top of standard HTML, CSS, and JavaScript and offers useful features to progressively enhance existing HTML pages.
Vue.js offers numerous features for writing Single Page Applications (SPAs) and complex web applications. With Vue, your developers can create markup that’s managed entirely by Vue.js using a progressive approach. They can use global components written using a special HTML template syntax to create reusable markup blocks. And if they want to define these components and get more control than the HTML syntax allows, they can write JSX or plain JavaScript functions.
Vue.js also allows developers to take advantage of built-in libraries for client-side routing and state management. Whenever required, they also have the freedom to select different routing/state management libraries based on their application requirements.
The Benefits of Vue.js Command Line Interface (CLI)
Vue.js comes with a CLI (Command Line Interface) to streamline development and simplify app creation by means of:
- Interactive project scaffolding.
- Upgradeable runtime dependency that can be configured via the in-project config file and extended via plugins.
- Numerous official plugins and tools in the front-end ecosystem.
- A GUI to create and manage projects.
The CLI provides numerous project configurations that can be used as-is, plus end-to-end testing libraries, easy-to-use routing systems, and Server-Side Rendering (SSR) to present fully-rendered web pages to search engine crawlers. But apart from preset configurations, you can also create your own for TypeScript, linting, and testing.
The Vue.js CLI includes a built-in development server so you can run your app locally and test it prior to deployment without configuring a server yourself. Plus, the various build tools work smoothly with sensible defaults, so you don’t have to waste time or effort on configurations and can focus on writing app code instead. If required, you can easily change the configuration of each tool without the need for ejecting.
The Vue.js CLI, combined with other front-end development tools, makes it easy to set up Vue.js. Some functionality is included by default, but you can also build code with a DRY (Don’t Repeat Yourself) logic and structure. Plus, it comes with several plugins that can be included when creating a new project, added to it later, or grouped into reusable presets.
The Benefits of Single File Components in Vue.js
Components play a crucial role in developing web apps with Vue.js.
Useful building blocks
They break up a large application into smaller and distinct building blocks. Developers can easily create these blocks and manage them separately. They can add and render components asynchronously or on-demand with Vue’s “lazy loading” feature, which is a great way to reduce the file size and HTTP request-response time.
Optimised code
It’s also easy to transfer data between components since Vue.js simplifies communication between component hierarchies. These smaller blocks make it easier to write, test, and optimise application code. The template, logic, and styles are inherently coupled inside each component. Such collocation makes components more cohesive and easier to maintain.
Global components and support for build-time tools
With the Vue.js framework, you don’t have to place your application template, logic, and styling code into separate files. Instead, you can group all these elements into a single global file ending with a .vue extension. As a result, your team can take advantage of build-time tools like Webpack or Browserify to add more sophisticated components to the web application.
These build tools automate the creation of executable applications from source code by compiling, linking, and packaging the code into an executable form. Developers can automate a number of day-to-day tasks such as downloading dependencies, compiling source code into binary code and then packaging it, running tests, and even deploying the application to production.
Preprocessors for feature-rich components
With the single file component structure, you can also take advantage of preprocessors like Pug, Babel, and Stylus to create cleaner and more feature-rich components. Also, since each component is written with HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, it is simpler and more readable.
What Makes Vue.js Better than Other Frontend Frameworks?
Apart from its versatile CLI and single file components, there are many other reasons why Vue.js is such a popular front-end framework. For one, it is as powerful as other older front-end frameworks despite its light and flexible avatar. Also, since it uses JavaScript, anyone who is already familiar with JavaScript can get started with Vue.js with very little onboarding or adjustment time.
Another reason for Vue’s popularity is that it provides a rich, incrementally-adoptable ecosystem that can seamlessly scale between a library and a full-featured framework. Vue.js is also a highly approachable framework with intuitive APIs and world-class documentation.
Vue.js is also highly performant with built-in reactivity. Its rendering system is compiler-optimised, so it rarely requires manual optimisation. Real-time functionality is also a breeze with Vue.js, so you can easily apply simple directives in your applications.
One of the most frequently-used capabilities in Vue.js is the ability to create computed properties. With such properties, you can easily modify, manipulate, and display data in a highly readable format while removing excess logic in templates.
Vue.js Security
Vue.js has a good history of disclosing and patching new security vulnerabilities - which are fortunately seemingly pretty rare. However, more recently, cross-site scripting (XSS) and regular expression denial of service (ReDoS) vulnerabilities have been discovered, so being informed about how they manifest and possessing the skills to close these vulnerabilities once their fixes have been issued is paramount.
How to use Vue.js securely
One way to steer clear of these vulnerabilities and ensure that the application remains secure is to always use the latest version of Vue and its official companion libraries. Vue also suggests several ways to maintain application security:
- Only use trusted component templates that you control entirely.
- Sanitise untrusted input in HTML (bind inner HTML), style (CSS), attributes (binding values), and resources (referring files) to prevent XSS attacks. Always ensure that user-provided URLs are sanitised by your backend before they are saved to a database.
- Use the “vue-sanitize” library to allow-list and sanitise user input values on your server.
- Avoid customising Vue libraries. If you do, make improvements and fixes to Vue libraries and share your changes with the community via a pull request.
- Keep all NPM packages in your Vue application up-to-date to avoid vulnerability.
- Avoid risky Vue API methods to safely generate HTML nodes.
- Instead of directly accessing a DOM element, use Vue’s escape hatches, such as
findDOMNodeand$refs.
Some other best practices to protect your Vue applications include:
- If you know the HTML is safe, explicitly render HTML content using a template, render function, or a render function with JSX.
- To keep users safe from clickjacking, allow full control over CSS only inside a sandboxed iframe, if really needed.
- Avoid rendering a
<script>element with Vue. - Audit dependencies to confirm that installed NPM packages are upgraded to the latest version.
Practical, Hands-on Vue.js Training with SecureFlag
Vue.js is a user-friendly, feature-rich, progressive, and powerful front-end development framework for web UIs. However, the security of Vue.js applications is only as good as the security awareness of those who create them. In other words, developers who don’t code securely will end up creating insecure Vue applications, with the resulting vulnerabilities in these applications opening up the organisation mainly to cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks.
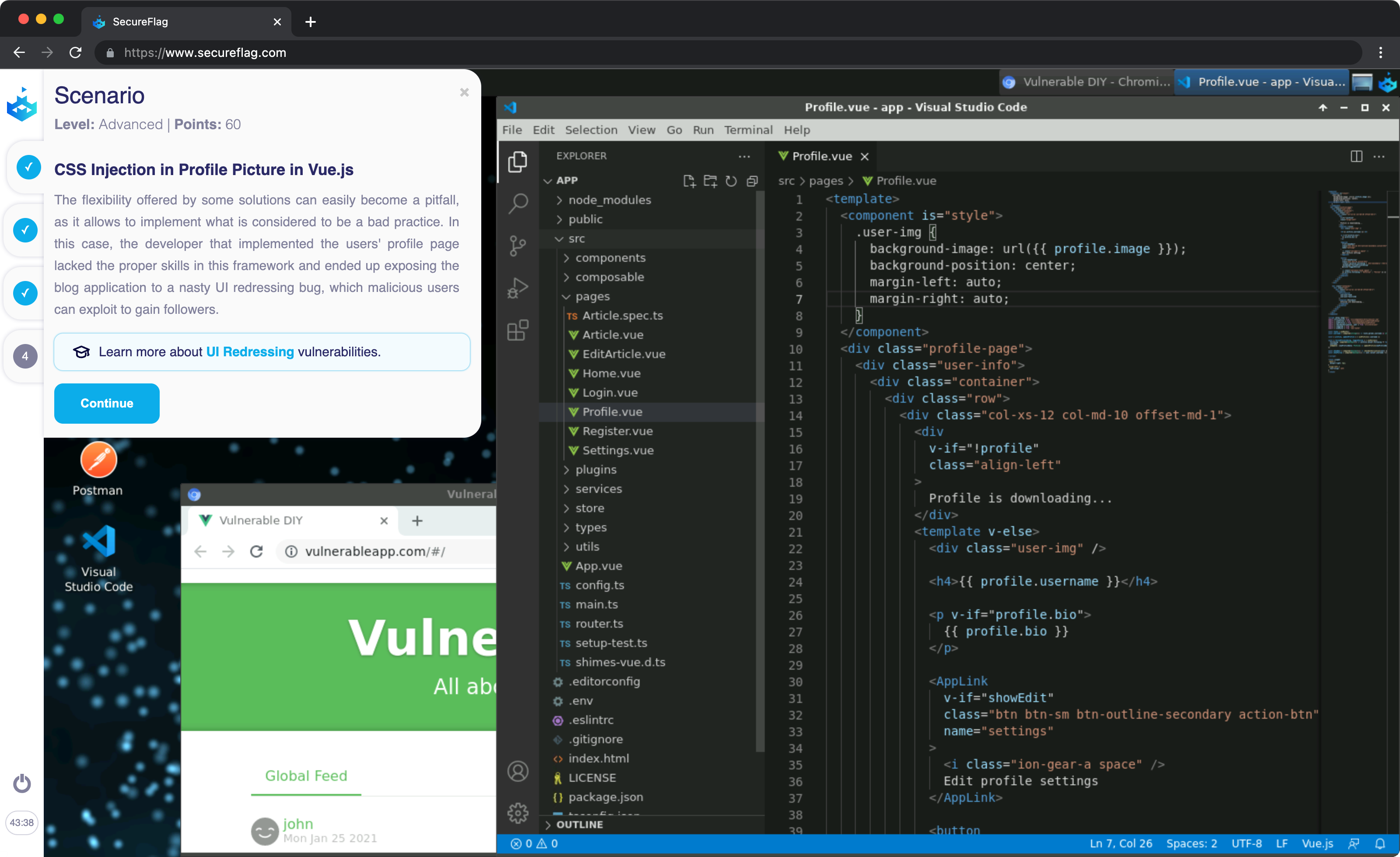
To avoid calamity from an ill-conceived Vue.js app, it’s vital to train your team on secure coding practices in Vue.js. But old-fashioned training programmes that are chock-full of boring videos and outdated examples are not enough to bring developers up-to-speed on today’s security challenges. To successfully overcome these challenges and create fully secure Vue.js UIs, developers need hands-on training that allows them to apply their learnings in the real world.
SecureFlag provides a 100% hands-on virtual development environment for Vue security awareness training. Developers learn how to identify and remediate threats through hands-on exercises for better learning retention and tangible results. To know how SecureFlag’s practical training programmes can boost your team’s secure coding capabilities, click here.


